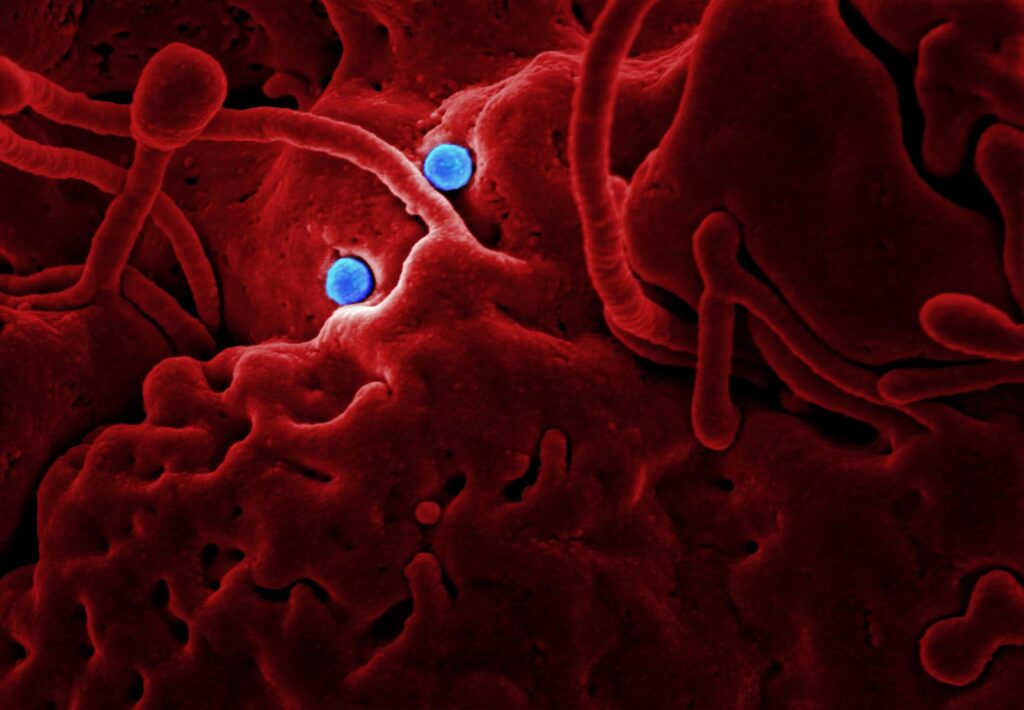
Osteomyelitis is a serious infection of the bone that can cause significant pain, swelling, and other complications if left untreated. This condition can affect anyone, from children to the elderly, and requires prompt medical attention to prevent the infection from spreading and causing more serious health problems. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and complications of osteomyelitis.
Causes and Risk Factors for Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis can occur when bacteria, viruses, or fungi enter the body and infect the bone tissue. The most common cause of this infection is bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus, which can enter the body through an open wound or a surgical site. Other risk factors for osteomyelitis include:
- Diabetes
- A weakened immune system
- Intravenous drug use
- A history of bone fractures or surgery
- Poor blood supply to the bone
- Radiation therapy
- Certain medical conditions, such as sickle cell anemia or HIV/AIDS
Symptoms and Signs of Osteomyelitis
The symptoms of osteomyelitis can vary depending on the severity and location of the infection. Some common signs and symptoms include:
- Pain and tenderness in the affected bone
- Swelling and redness around the affected area
- Fever and chills
- Fatigue
- Night sweats
- Limited movement or stiffness in the affected area
- Drainage from the affected area
It is important to note that some individuals with osteomyelitis may not experience any symptoms, especially if the infection is chronic or has been present for a long period of time.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Osteomyelitis
If you suspect that you or a loved one has osteomyelitis, it is important to seek medical attention right away. Your doctor will likely perform a physical exam and order several tests to confirm the diagnosis, including:
- Blood tests to check for signs of infection
- X-rays to look for bone abnormalities
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans to get a more detailed view of the affected area
- Bone biopsy to determine the type of bacteria causing the infection
Treatment for osteomyelitis typically involves a combination of antibiotics and surgery. Antibiotics are used to fight the infection, while surgery may be necessary to remove any infected tissue or bone. In some cases, a bone graft or other reconstructive surgery may be necessary to repair the damaged bone tissue.
Prevention and Complications of Osteomyelitis
There are several steps you can take to help prevent osteomyelitis, including:
- Properly treating any open wounds or injuries
- Practicing good hygiene, such as washing your hands regularly
- Maintaining good dental health
- Managing chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes or sickle cell anemia
If left untreated, osteomyelitis can lead to serious complications, such as:
- Chronic pain
- Bone deformities
- Septicemia, or blood poisoning
- Joint infections
- Amputation
In conclusion, osteomyelitis is a serious infection of the bone that requires prompt medical attention to prevent further complications. If you suspect that you or a loved one may have osteomyelitis, seek medical attention right away. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and complications of osteomyelitis, you can take steps to protect your bone health and overall wellbeing.