If you’ve ever felt a sharp twinge or deep ache in your calf, you’re not alone. Studies show that calf injuries account for up to 12% of all muscle injuries in runners and active individuals. In Edmonton and Sherwood Park, where hiking, cycling, and weekend races are part of the lifestyle, understanding your gastrocnemius muscle is essential to staying active and injury-free.
In this guide, you’ll learn what your gastrocnemius muscle does, how to spot trouble signs, and what to do when pain strikes — including when to worry about calf pain and how to speed up your recovery safely.
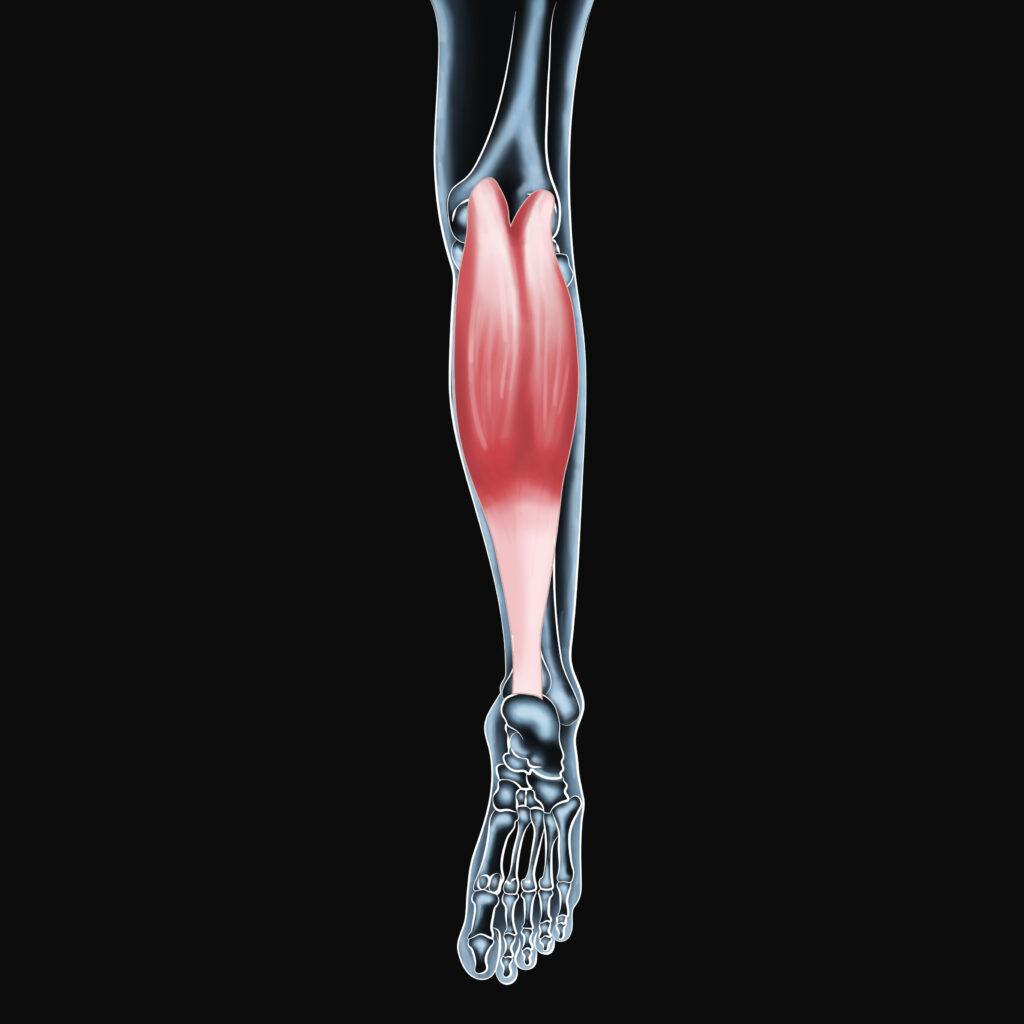
Understanding Your Gastrocnemius Muscle
The gastrocnemius muscle is one of the two primary muscles that form the calf, located at the back of your lower leg. It originates just above your knee and connects to the heel via the Achilles tendon. Together with the soleus muscle, the gastrocnemius plays a critical role in activities like:
- Walking and running
- Jumping
- Pushing off during sports
- Balancing on your toes
Without a healthy gastrocnemius, even simple activities like hiking through Edmonton’s river valley trails or training at Sherwood Park gyms become challenging.

What Happens When the Gastrocnemius Muscle Is Injured?
Active individuals often encounter common gastrocnemius problems, including:
Strains and Tears
A sudden sprint during a soccer game or a sharp push-off while trail running can strain the calf muscle or cause minor tears. Symptoms often include sudden sharp pain, swelling, and difficulty standing on tiptoes.
Real-World Example:
An Edmonton marathon runner reported a sudden ‘pop’ in his calf 10K into his race. A mild tear in the gastrocnemius was diagnosed — highlighting the importance of warming up thoroughly.
Muscle Cramps
Cramping is common during high-intensity activities, especially in hot weather. A cramping gastrocnemius can leave you sidelined mid-activity.
Tightness and Reduced Mobility
Long hours spent cycling, running, or even standing can tighten the gastrocnemius. This limits flexibility, increases the risk of injury, and can cause discomfort.
When to Worry About Calf Pain
While minor soreness after exercise is normal, certain symptoms suggest it’s time to seek professional help:
- Sudden, severe calf pain without trauma
- Persistent swelling or bruising
- Pain that worsens with activity
- Difficulty flexing the ankle or bearing weight
Knowing when to worry about calf pain can help prevent minor issues from turning into long-term problems. If in doubt, consulting a therapist at our Sherwood Park massage therapy clinic can make a world of difference.
How to Stretch Your Gastrocnemius Muscle
Effective stretching improves flexibility, reduces injury risk, and speeds recovery. Here are easy, therapist-approved stretches for your gastrocnemius:
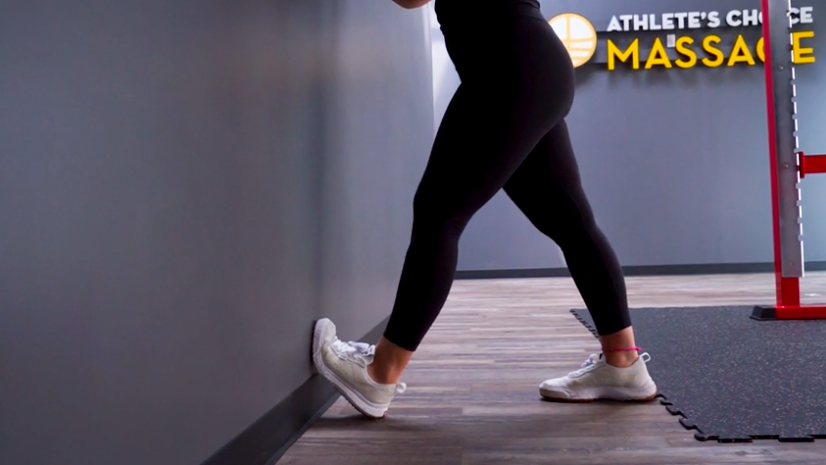
1. Standing Calf Stretch
- Stand facing a wall, arms extended.
- Step back with one foot, keeping your heel flat.
- Lean forward slightly until you feel a stretch.
- Hold for 30 seconds. Switch legs.
2. Seated Towel Stretch
- Sit on the floor with legs straight.
- Loop a towel around the ball of your foot.
- Gently pull the towel toward you.
- Hold for 30 seconds per leg.
3. Downward Dog Yoga Stretch
- Start in a plank position.
- Push your hips up and back to form an inverted “V.”
- Press heels toward the ground for a deep calf stretch.
Tip: Always warm up lightly before stretching to avoid injury.

How to Rehab a Gastrocnemius Injury
Rehabbing the gastrocnemius muscle effectively means balancing rest and gradual strengthening. Follow these steps:
1. Rest and Protect
Avoid activities that stress the calf, especially during the first 48–72 hours post-injury.
2. Ice and Elevate
Apply an ice pack (wrapped in a towel) for 15–20 minutes every few hours. Elevate your leg above heart level.
3. Compression Support
Use a compression bandage to control swelling and stabilize the injured calf muscle.
4. Gradual Stretching
Begin with gentle stretches under professional guidance, such as those used in our therapeutic massage treatments.
5. Strengthening Exercises
Once cleared by a therapist, introduce light calf raises, resistance bands, and balance exercises to rebuild strength safely.
For stubborn injuries, advanced treatments like shockwave therapy for muscle pain can promote faster healing.
Staying Strong for an Active Lifestyle
Supporting your gastrocnemius muscle health is critical if you love staying active across Edmonton and Sherwood Park. Whether you’re sprinting down a soccer field, cycling through Mill Creek Ravine, or hiking Elk Island trails, caring for your calf muscles keeps you moving without setbacks.
If you’re dealing with calf pain or want to optimize performance, the team at Athlete’s Choice Massage is ready to support your goals with tailored treatments that match your active lifestyle.