Ligaments are a vital component of the human body’s connective tissue. They are the fibrous bands of tissue that connect bones to each other, providing stability to the joints. Ligaments are essential for maintaining the proper alignment of bones and preventing excessive movement that can cause injury. In this article, we will take a closer look at ligaments, their functions, common injuries, diagnosis, treatment options, and how to prevent them.
What Are Ligaments and Their Functions?
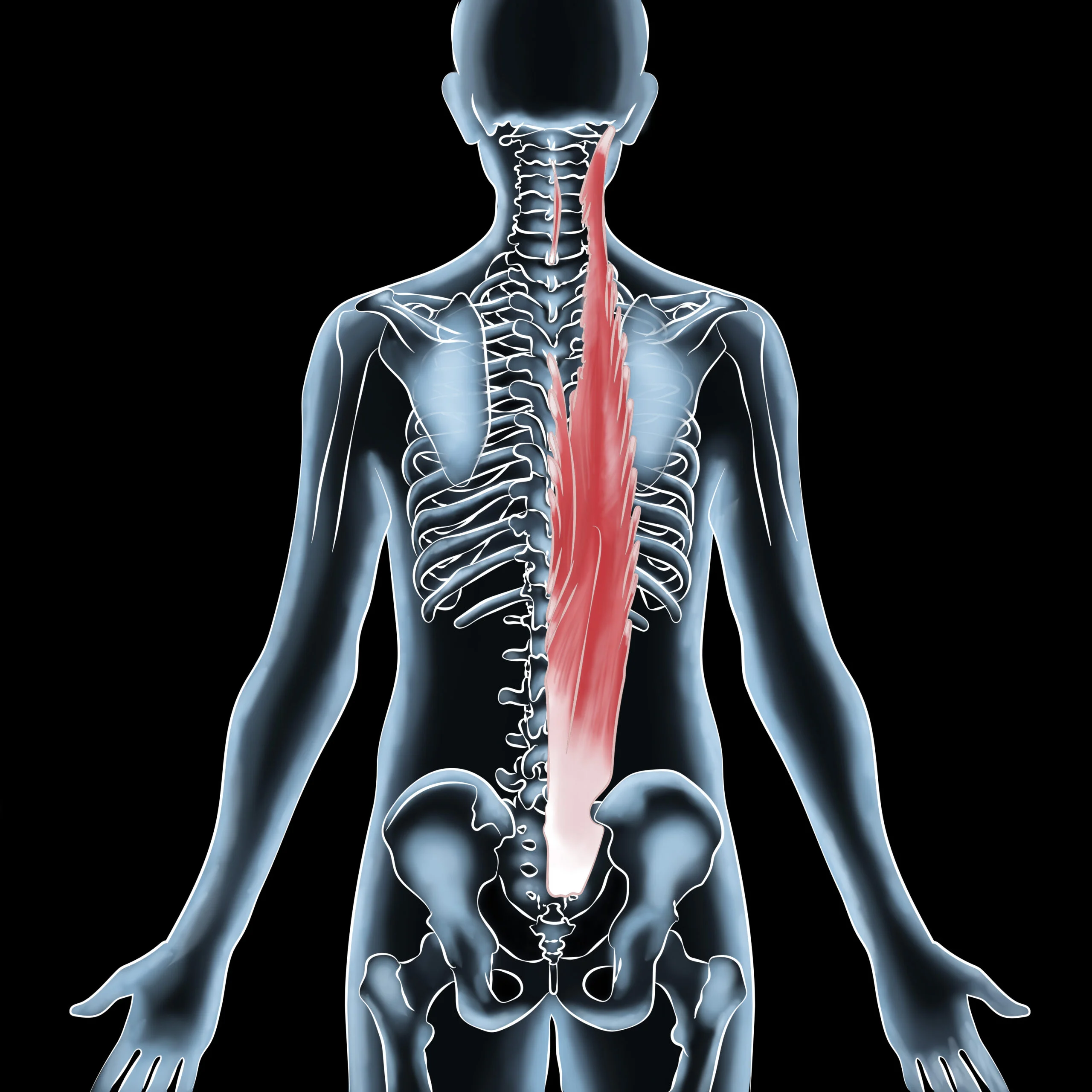
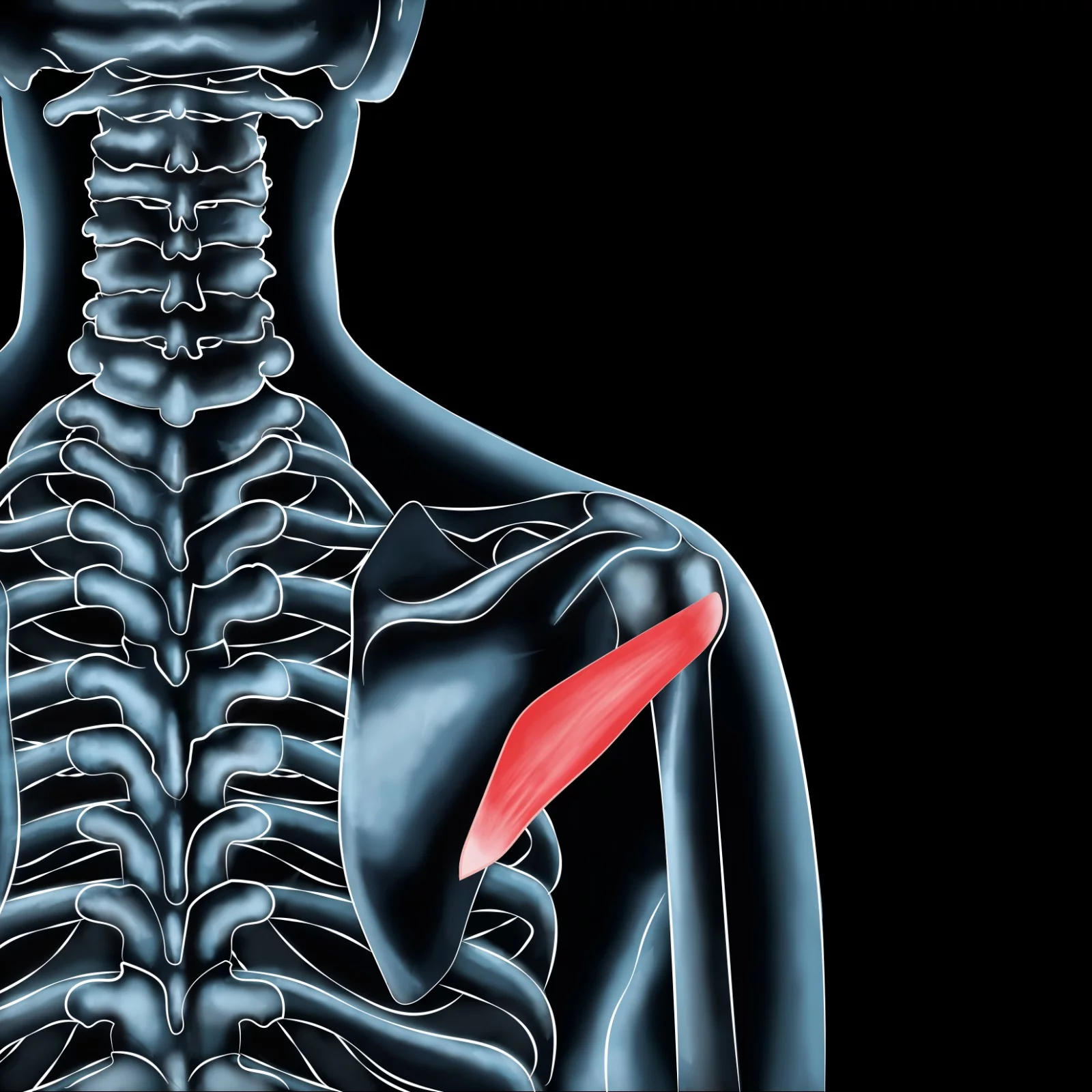
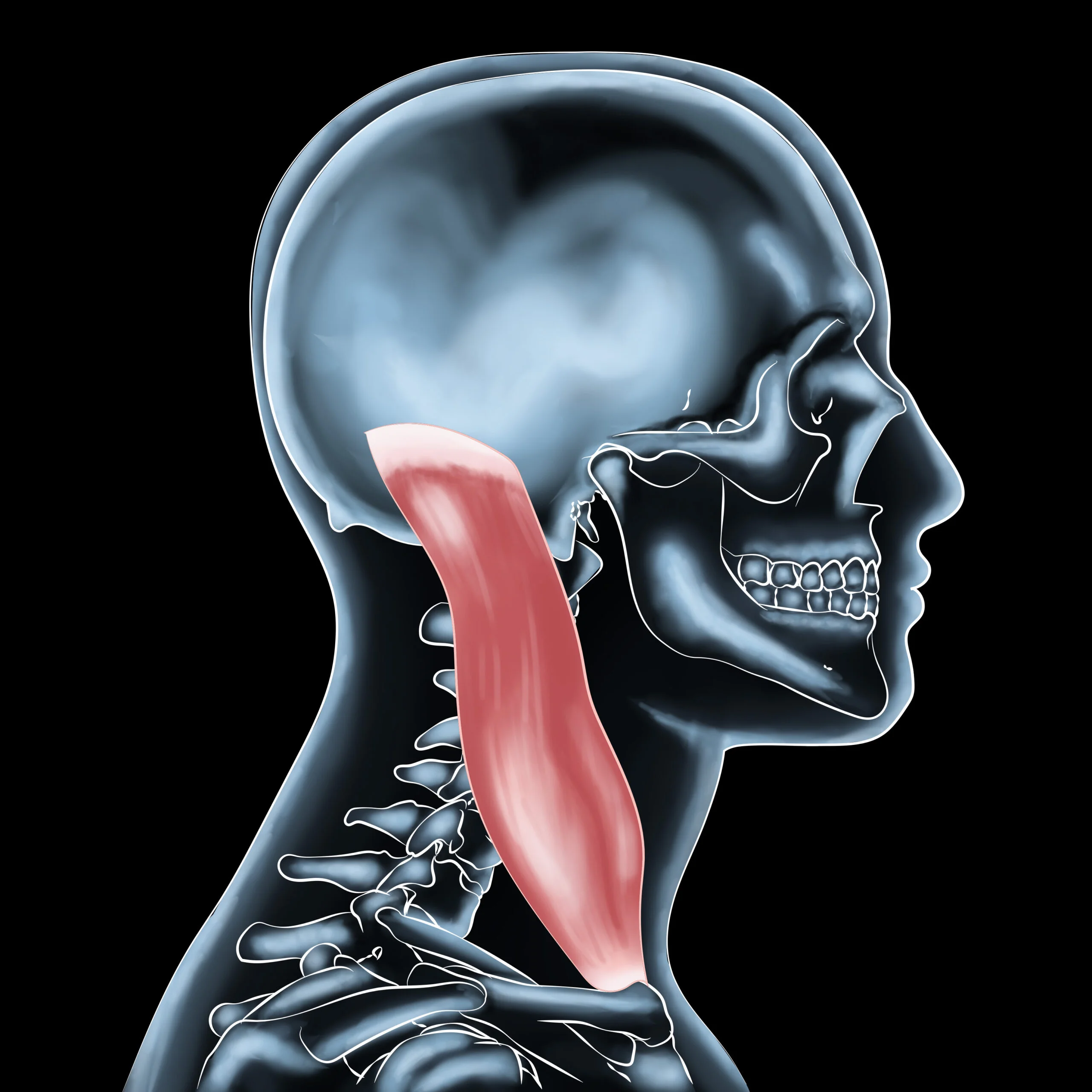
Ligaments are fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to each other in a joint. They are composed of collagen, elastin, and other proteins that give them their strength and flexibility. Ligaments are responsible for holding bones in the correct position and preventing them from moving too far in any direction. In other words, they provide stability to the joints.
Ligaments are located in various parts of the body, such as the knees, ankles, wrists, elbows, and shoulders. They are essential for maintaining proper joint function during physical activities, such as running, jumping, and twisting. When a person moves, the muscles contract, pulling on the bones. The ligaments prevent excessive movement and ensure that the bones are in the correct alignment.
Common Ligament Injuries and Their Symptoms
Ligament injuries are common, especially in people who participate in sports or activities that involve repetitive stress on the joints. The most common ligament injuries include sprains and tears. A sprain is a stretching or tearing of a ligament, while a tear is a complete rupture of the ligament.
The symptoms of a ligament injury can vary depending on the severity of the injury. The most common symptoms include pain, swelling, bruising, and limited mobility. In some cases, there may be a popping sound or sensation when the injury occurs. The severity of the symptoms can indicate the severity of the injury.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Ligament Injuries
The diagnosis of a ligament injury typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests. During the physical examination, the doctor will look for swelling, tenderness, and limited range of motion. They may also move the joint to check for stability and pain.
Imaging tests, such as X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound, may be ordered to determine the severity of the injury. X-rays can detect any bone damage, while an MRI or ultrasound can detect soft tissue damage, such as ligament tears.
Treatment for ligament injuries typically involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). The RICE method helps to reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation. Depending on the severity of the injury, the doctor may recommend immobilization of the joint with a brace or cast to allow the ligament to heal properly. Physical therapy may also be recommended to improve flexibility and strengthen the muscles surrounding the joint.
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair a torn ligament. Surgery may involve reconnecting the torn ends of the ligament or replacing it with a graft from another part of the body. The recovery time for surgery can vary depending on the severity of the injury and the type of surgery performed.
After surgery, a period of rest and rehabilitation is necessary to ensure proper healing and to regain strength and function in the affected area. The rehabilitation program may include physical therapy, exercises to improve range of motion and strength, and techniques to reduce pain and inflammation.
Preventing Ligament Injuries: Tips and Exercises
While some ligament injuries may be unavoidable, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of injury. Here are some tips and exercises to help prevent ligament injuries:
- Warm-up and stretch before physical activity: Warming up before physical activity can help prepare your body for movement and reduce the risk of injury. Stretching can also help improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension.
- Wear appropriate footwear: Wearing the appropriate footwear for your activity can help provide support and stability to your feet and ankles, reducing the risk of sprains and strains.
- Use proper technique: Using proper technique during physical activity can help reduce the risk of injury. For example, proper form when lifting weights can help reduce the risk of a knee or back injury.
- Incorporate balance and stability exercises: Incorporating exercises that improve balance and stability, such as yoga or Pilates, can help improve overall body control and reduce the risk of injury.
- Gradually increase intensity and duration of physical activity: Gradually increasing the intensity and duration of physical activity can help your body adapt to the demands of the activity, reducing the risk of injury.
Conclusion
Ligaments play a crucial role in providing stability and support to our joints and bones. While ligament injuries can be painful and limit mobility, there are effective treatment options available. It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have a ligament injury, as prompt treatment can help prevent further damage and improve your chances of a full recovery. By taking steps to prevent ligament injuries, you can reduce your risk of injury and enjoy a healthy and active lifestyle.