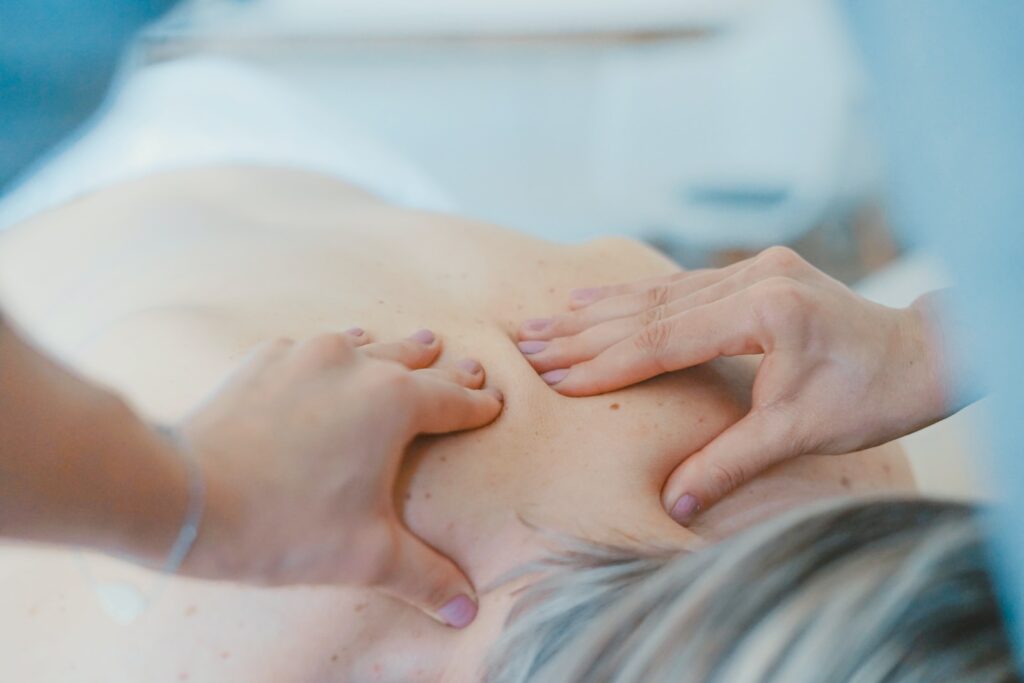
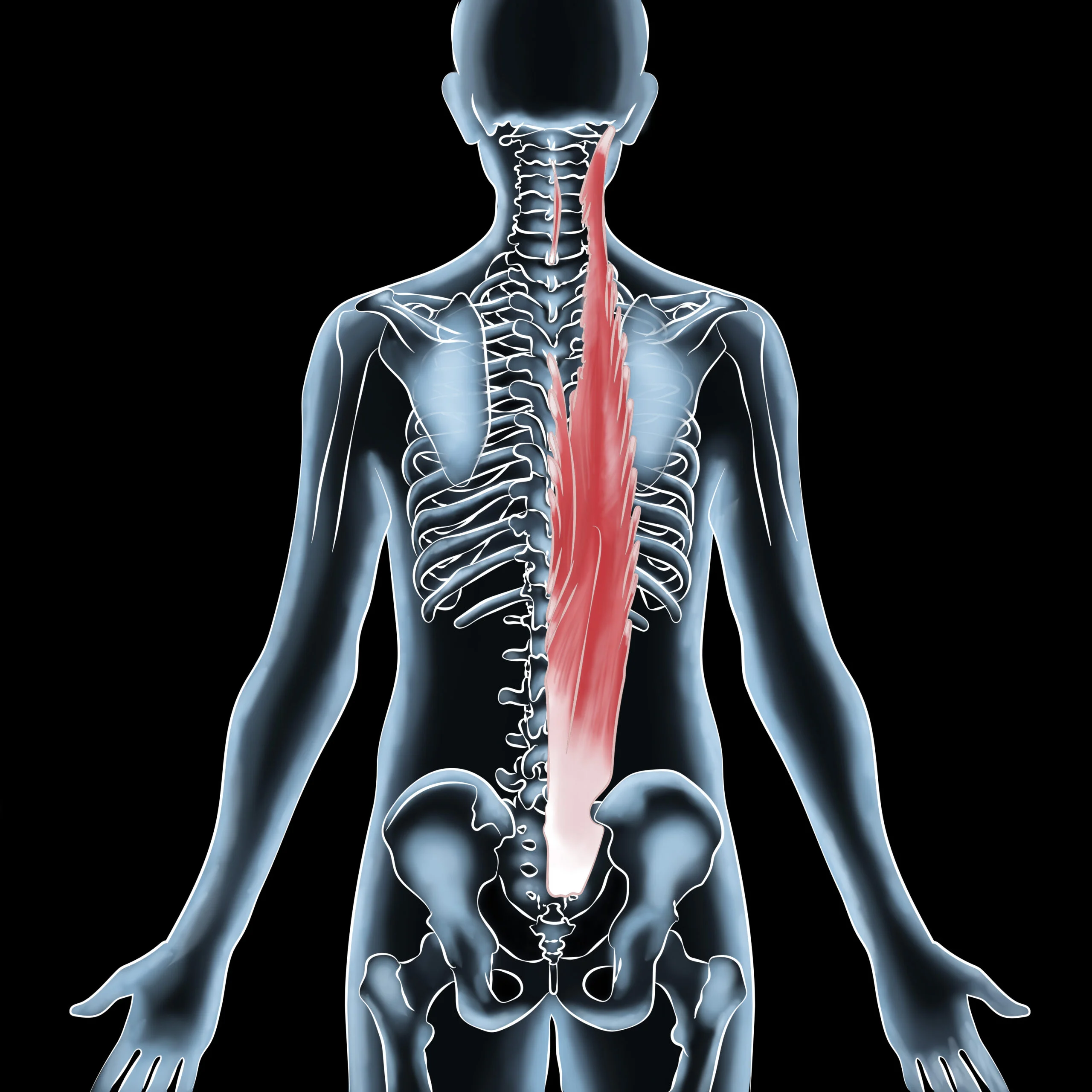
Muscle knots, also known as myofascial trigger points, can be frustrating and painful condition. Understanding what causes muscle knots, how to identify the symptoms, and how to treat and prevent them is essential for those who suffer from this condition. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention of muscle knots and the science behind this mysterious condition.
Causes of Muscle Knots: Common Triggers and Risk Factors
Muscle knots can be caused by a variety of factors, including overuse or repetitive use of muscles, poor posture, stress, and injury. Here are some common triggers and risk factors:
- Overuse or Repetitive Use: Repeatedly using the same muscle or muscle group can cause muscle knots to form. This is common in athletes or individuals who perform repetitive motions in their daily lives, such as typing on a computer.
- Poor Posture: Poor posture, such as slouching or hunching over, can lead to muscle knots in the back, neck, and shoulders.
- Stress: Stress can cause muscles to tense up, leading to the development of muscle knots. This is especially common in the neck and shoulders.
- Injury: Trauma to a muscle or muscle group can cause muscle knots to form. This can include sprains, strains, or direct impact on the muscle.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Muscle Knots: Identifying the Problem
The symptoms of muscle knots vary from person to person, but common symptoms include localized pain or tenderness, stiffness, weakness, and reduced range of motion in the affected muscle. In some cases, muscle knots can also cause referred pain, where the pain is felt in a different part of the body than where the knot is located.
To diagnose muscle knots, a healthcare professional will perform a physical exam and assess the affected area for tenderness, stiffness, and restricted range of motion. They may also ask the patient to perform certain movements to assess the muscle’s function. In some cases, imaging tests such as X-rays, MRIs, or ultrasound may be necessary to rule out other potential causes of the symptoms.
Treatment and Prevention of Muscle Knots: Relief and Management
Treatment for muscle knots typically involves a combination of manual therapies, such as massage or trigger point release, and exercises to stretch and strengthen the affected muscles. In some cases, medication may also be prescribed to manage pain and inflammation.
Prevention of muscle knots involves maintaining proper posture, stretching regularly, and taking breaks during repetitive activities to rest and stretch muscles. It’s also important to stay hydrated and maintain a healthy diet to support muscle health.
The Science Behind Muscle Knots: Exploring the Physiology
Muscle knots are caused by the contraction of muscle fibers and the formation of adhesions between muscle fibers and surrounding tissues. These adhesions can cause localized pain and inflammation, which can lead to the development of muscle knots.
The exact cause of muscle knots is not fully understood, but it is believed that a combination of factors, including muscle overuse, injury, and stress, can contribute to the development of muscle knots.
Conclusion
Muscle knots can be a frustrating and painful condition, but understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention can help individuals manage their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life. Seeking medical attention and working with a healthcare professional can help individuals identify the problem and develop an effective treatment plan. By taking steps to prevent muscle knots and maintain proper muscle health, individuals can reduce their risk of developing muscle knots and improve their overall well-being.