The quadriceps muscles, commonly referred to as the “quads,” play a pivotal role in nearly every leg movement—from walking and running to powerful jumps. Unfortunately, the quads are also susceptible to strains, injuries, and overuse problems, especially in active individuals. Keeping your quad muscles strong and healthy can enhance your performance, reduce your risk of injury, and support better mobility as you age.
This article will break down the essentials of quadriceps health, common issues, and effective stretching and rehabilitation techniques for stronger, more resilient quad muscles.
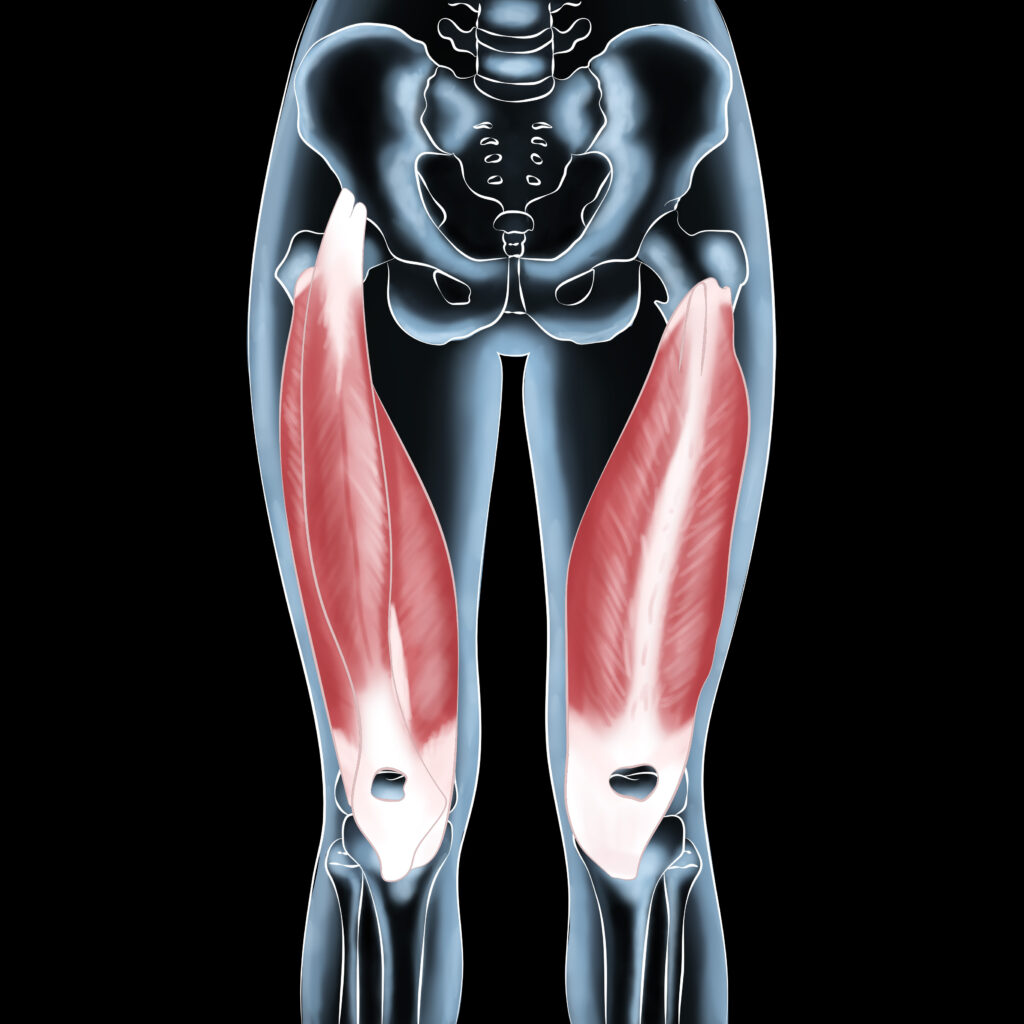
Understanding Your Quadriceps Muscles: Functions & Importance
The quads muscle group, located at the front of your thigh, is the largest muscle group in the body. Consisting of the rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius, and vastus medialis, the quadriceps muscle primarily enables knee extension and hip flexion. These actions are essential for basic activities like walking and climbing stairs and for high-impact movements, including sprinting and jumping. Additionally, the quads stabilize the knee, protecting it from stress and injury during weight-bearing activities.
Keeping your quadriceps muscles strong is vital for both performance and injury prevention. For active individuals in Edmonton and Sherwood Park, where outdoor sports and activities are part of the lifestyle, prioritizing quad health ensures you’re always ready for action.

Common Quadriceps Issues and Their Solutions
Regular activity can sometimes lead to quad muscle problems. Here’s a quick look at common issues and ways to manage them:
1. Strains
Overuse or sudden forceful movements can cause quad strains, leading to pain, swelling, and restricted mobility. Rest, ice, and gradual stretching can help recovery. If the strain is severe, seek professional guidance.
2. Tendinitis
Often caused by repetitive motions, tendinitis involves inflammation in the quadriceps tendons, particularly around the knee. Applying ice, resting, and strengthening exercises can be beneficial. Consider shockwave therapy to target inflammation and speed up healing.
3. Contusions (Bruises)
Direct impacts, common in contact sports, may result in bruising. RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) can help reduce swelling and discomfort. For ongoing pain or limited mobility, consult a professional.
4. Atrophy
Inactivity, whether due to an injury or surgery, can lead to muscle atrophy. Gradual strengthening exercises, often guided by a therapist, are essential. Consider therapeutic massage for muscle recovery and improved mobility.
Effective Quadriceps Stretches for Flexibility and Injury Prevention
Regularly stretching your quadriceps muscles can enhance flexibility, relieve tightness, and prevent injuries. Try these stretches:
Standing Quad Stretch
Stand tall, grabbing one ankle and gently pulling it toward your glutes. Keep your knees together and avoid arching your back. Hold for 30 seconds, then switch sides.
Pigeon Pose
Place one leg forward, bent at the knee, while extending the opposite leg back. Lower your hips toward the floor, allowing a deep stretch along the front thigh of the extended leg.
Wall Quad Stretch
Place your foot against the wall behind you, keeping your knee on the ground. Lean slightly forward to stretch the quads deeply. Hold each stretch for 30 seconds.
Incorporating these stretches into your routine can help you maintain flexibility and reduce the risk of muscle strain.
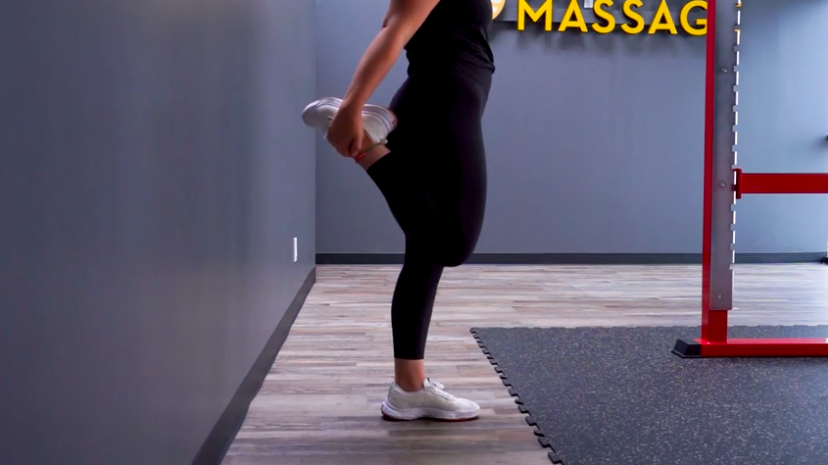

Rehabilitation Tips for Quadriceps Muscle Recovery
Recovering from a quadriceps injury requires patience and a systematic approach. Here are steps to aid your recovery:
- Rest & Ice
Begin with rest and apply ice to reduce inflammation. Keep your leg elevated when possible. - Gentle Stretches
Once initial pain subsides, start gentle quad stretches to restore flexibility. Avoid forcing the stretch to prevent further injury. - Gradual Strengthening
Rebuild strength through low-resistance exercises like leg extensions or bodyweight squats, progressing to more challenging movements as you improve. - Professional Assistance
If pain persists, consulting a professional is essential. Sport massage can also support recovery by increasing blood flow to the injured area, enhancing muscle healing.
To make recovery easier, check out Athlete’s Choice Massage in Sherwood Park, where their team can guide you through rehabilitation and preventative care.
Keep Your Quadriceps Strong and Ready for Adventure
Maintaining strong, flexible, and healthy quadriceps muscles is essential for an active lifestyle, especially in the Edmonton and Sherwood Park areas, where outdoor activities are abundant. Prioritize quad health with regular stretching, balanced workouts, and, when necessary, professional guidance to keep your muscles resilient and ready for any adventure.