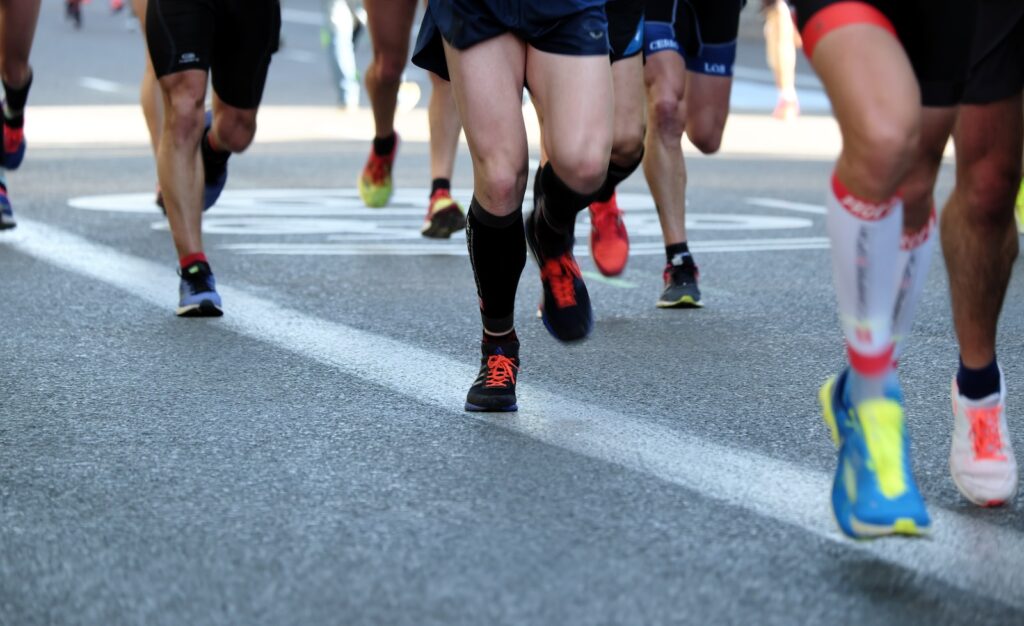
Running is a popular form of exercise that provides numerous physical and mental health benefits. However, as with any physical activity, running comes with its own set of risks and potential injuries. Understanding the muscles used in running, common running injuries, and recovery strategies can help you stay healthy, active, and injury-free.
Anatomy and Function of Running Muscles
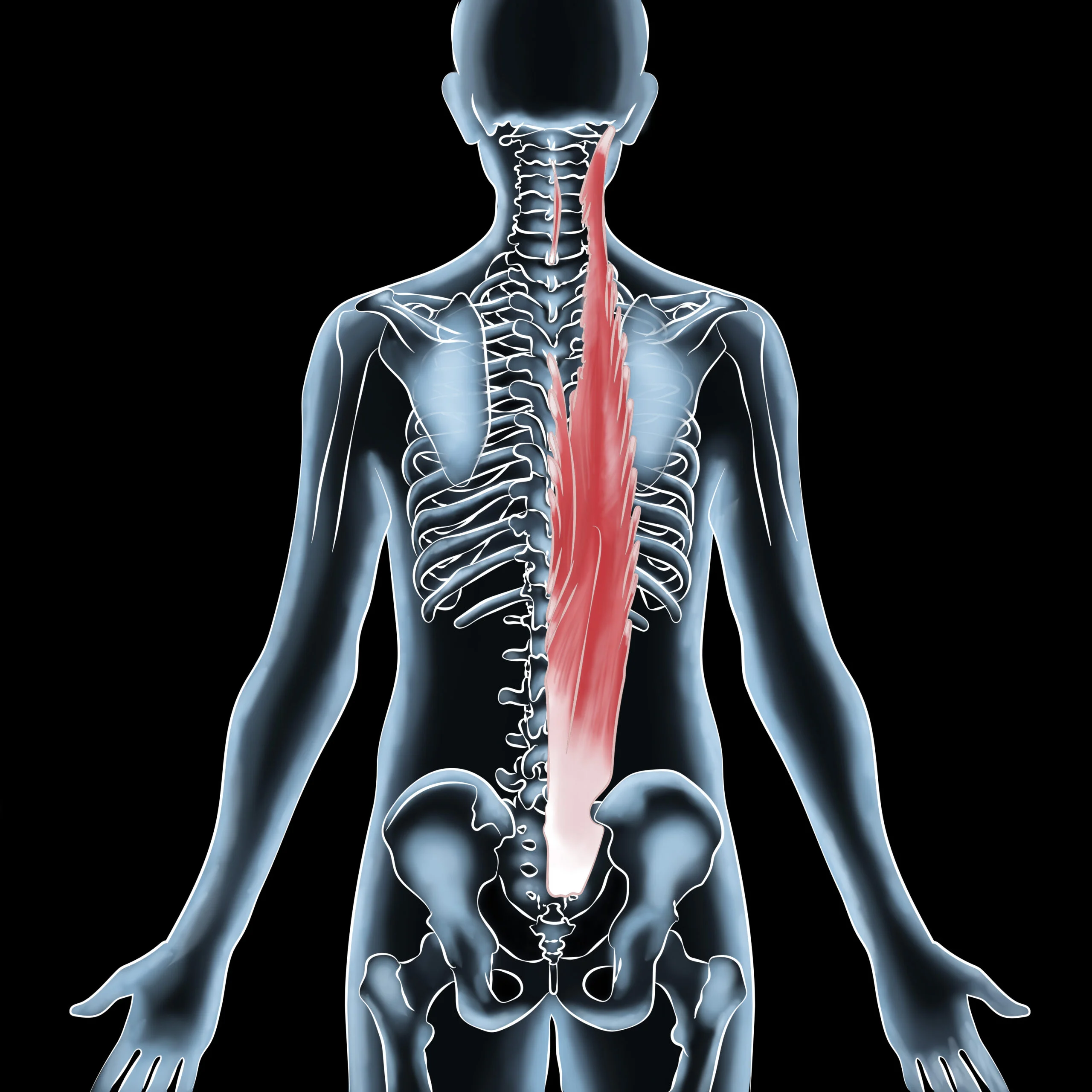
Running is a full-body workout that engages numerous muscle groups, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, calves, abdominals, and upper body. These muscles work together to propel the body forward and maintain balance and stability.
The quadriceps, located in the front of the thigh, are responsible for extending the leg and providing power and speed during running. The hamstrings, located in the back of the thigh, work in opposition to the quadriceps to flex the knee and stabilize the hip.
The glutes, or buttock muscles, are important for maintaining balance and stability during running. The calves, located in the back of the lower leg, are responsible for pushing off the ground and providing forward momentum.
Common Running Injuries and Prevention Techniques
Despite the many benefits of running, it can also be associated with a variety of injuries. Some of the most common running injuries include shin splints, plantar fasciitis, IT band syndrome, runner’s knee, and Achilles tendonitis.
To prevent running injuries, it is important to incorporate proper warm-up and cool-down routines, stretch regularly, gradually increase mileage and intensity, and wear proper footwear. Strength training and cross-training can also help prevent injuries by building muscular endurance and improving overall fitness.
Effective Treatments for Running-Related Injuries
If you do experience a running-related injury, seeking prompt and effective treatment is important for a full and speedy recovery. Treatment options may include rest, ice, compression, and elevation, as well as physical therapy, medication, and in severe cases, surgery.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of treatment for your specific injury. Early intervention and proper treatment can help prevent the injury from becoming chronic or leading to long-term damage.
Recovery Strategies for Runners
Recovering from a running injury can be frustrating and challenging, but taking the appropriate steps can help speed up the recovery process and prevent future injuries. Rest and relaxation are key components of recovery, as well as following a rehabilitation plan prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Cross-training, such as cycling or swimming, can also be helpful for maintaining cardiovascular fitness and building strength while allowing the injured area to heal. Gradually increasing activity levels and incorporating preventative measures can also help reduce the risk of re-injury.
Conclusion
Running is a great way to improve physical fitness, mental health, and overall well-being. However, it is important to take steps to prevent injuries, understand the muscles used in running, and seek prompt and effective treatment when injuries do occur. With proper care and attention, runners can stay healthy, active, and injury-free.