The Vital Role of Hamstring Muscles in Movement
Hamstring injuries are common, especially in those who engage in physical activities like running, jumping, and quick directional changes. The hamstring muscles, located in the back of the thigh, are essential for bending the knee and extending the hip. When these muscles are strained or injured, mobility and comfort are greatly impacted.
This guide will explain where the hamstring is located, the symptoms of injury, treatment options, and strategies to prevent future issues.

Anatomy of the Hamstring Muscles
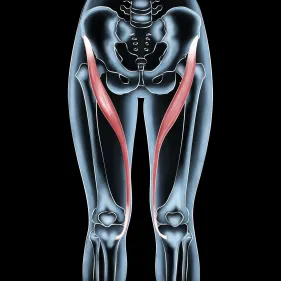
The hamstring muscles consist of three key components:
- Biceps Femoris: Found on the outer thigh, responsible for bending the knee and aiding leg rotation.
- Semitendinosus: Runs along the inner thigh, assisting with knee bending and hip extension.
- Semimembranosus: Also on the inner thigh, working in tandem with the semitendinosus.
If you’ve wondered, “Where is the hamstring located?” it starts at the pelvis (ischial tuberosity) and attaches to the lower leg bones, spanning the back of the thigh.
Symptoms of Hamstring Injuries
Hamstring injuries range from mild strains to severe tears. Common symptoms include:
- A sharp or sudden pain in the back of the thigh.
- Swelling or bruising in the affected area.
- Tenderness or difficulty walking.
- A “popping” sensation at the time of injury.
For severe injuries, it’s vital to consult a healthcare professional immediately.
Treatment Options for Hamstring Injuries
Recovery from a hamstring injury depends on its severity. Common treatment methods include:
- Rest and Ice: Resting the leg and applying ice can alleviate swelling and pain for minor strains.
- Compression and Elevation: Using compression bandages and keeping the leg elevated reduces swelling.
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises improve strength and flexibility, aiding recovery.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relief such as ibuprofen can reduce inflammation.
- Surgery: Reserved for cases involving complete tears of the hamstring muscle.
Complement your recovery with therapeutic massage therapy to enhance blood flow and support healing.
Preventing Hamstring Injuries
Prevention is the best approach to avoiding painful setbacks. Follow these steps to protect your hamstrings:
- Warm Up Before Exercise: Incorporate dynamic stretches and light cardio to prepare muscles.
- Strengthen the Hamstrings: Include exercises like deadlifts and bridges to build resilience.
- Practice Proper Form: Focus on technique during sports and workouts to minimize strain.
- Gradual Progression: Avoid sudden increases in intensity or duration when starting new activities.
- Regular Rest: Allow time for muscle recovery between sessions.
To keep your muscles healthy and balanced, explore deep tissue massage therapy for long-term injury prevention.
Support for Long-Term Recovery
If you’re recovering from an injury or want to prevent future strains, visit Sherwood Park massage clinics for expert care. Professional therapists can help improve muscle health and prevent recurring injuries.
Caring for Your Hamstring Health
Your hamstring muscles are vital for movement and physical activity. Taking steps to strengthen and protect them can help you avoid injuries and maintain an active lifestyle. Whether you’re recovering from an injury or seeking preventive care, professional massage therapy can support your overall muscle health.
Explore Athlete’s Choice Massage locations in Sherwood Park and Edmonton for expert care tailored to your needs.