Why Shoulder Pain Affects Active Lifestyles
For athletes and active individuals, maintaining mobility and strength in every muscle is essential to performance, especially for those in the Edmonton and Sherwood Park areas who may regularly engage in outdoor sports or fitness activities. Supraspinatus pain—a common but often overlooked source of shoulder discomfort—can disrupt daily routines and hinder athletic progress. Often tied to the supraspinatus muscle in the rotator cuff, this pain can result from overuse, incorrect posture, or sudden impact injuries. In this article, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and strategies for managing supraspinatus muscle pain, with actionable advice for preventing further strain.
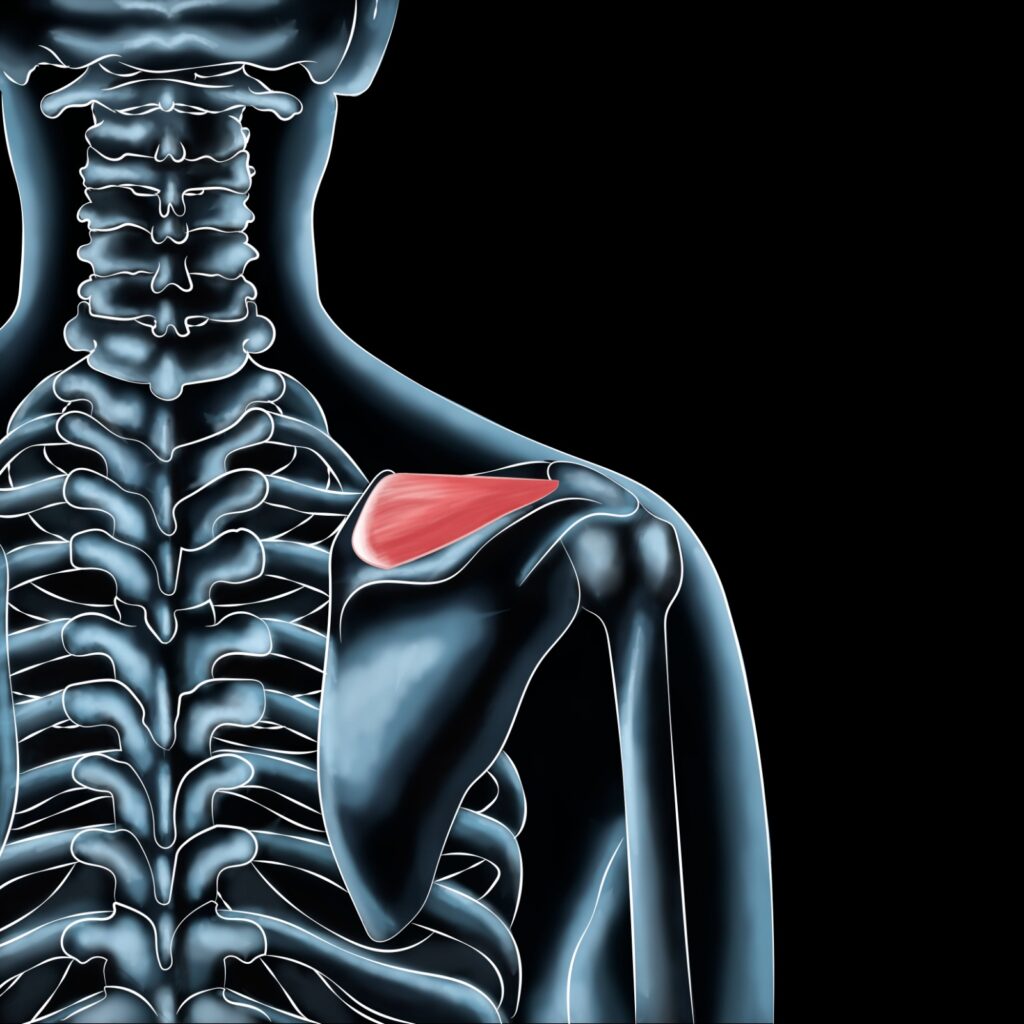
Understanding the Supraspinatus Muscle: Its Role in Shoulder Stability
The supraspinatus muscle is one of four muscles that make up the rotator cuff, responsible for shoulder stabilization and movement. Located on the upper shoulder blade, this muscle plays a crucial role in lifting the arm outward and rotating it slightly—essential movements for activities like swimming, tennis, and lifting. Injuries or strains to this muscle can severely limit an athlete’s ability to perform even simple shoulder movements without pain.

Common Issues Affecting the Supraspinatus Muscle
- Tendinitis: Frequent in those who perform repetitive overhead movements, tendinitis inflames the tendons of the supraspinatus, leading to stiffness and pain.
- Muscle Tears: Sudden impacts or chronic overuse can cause partial or complete tears, resulting in significant weakness and discomfort.
- Impingement Syndrome: When the supraspinatus muscle becomes compressed, often due to inflammation or bone spurs, it causes pain during shoulder movements.
- Frozen Shoulder: Also known as adhesive capsulitis, this condition restricts shoulder movement and may cause intense pain when lifting or rotating the arm.
Signs and Symptoms of Supraspinatus Muscle Pain
Identifying supraspinatus muscle pain early can help prevent further injury. Key symptoms include:
- Dull ache along the top of the shoulder, especially noticeable after physical activity.
- Weakness when attempting to lift or rotate the arm outward.
- Pain when sleeping on the affected shoulder.
- Difficulty reaching overhead or across the body.
Effective Tactics to Manage and Relieve Supraspinatus Pain
Taking proactive steps to manage supraspinatus pain can significantly aid in recovery and prevent chronic discomfort. Here are actionable methods for managing this condition:
1. Rest and Ice
- Rest: Limit activities that strain the shoulder to allow the muscle to heal.
- Ice Application: Apply ice for 15-20 minutes several times daily to reduce inflammation.
2. Stretching Exercises
- Doorway Stretch: Stand in a doorway, place your hands on the frame, and step forward to stretch the shoulder.
- Cross-Body Stretch: Gently pull one arm across your body with the opposite hand to stretch the supraspinatus.
- Behind-Back Arm Stretch: Reach one arm behind your back, gently pulling it closer with the other hand.
3. Strengthening Exercises
- Prone T Exercise: Lie face-down with your arms out to the side in a “T” position. Lift your arms off the ground slightly, hold, and release.
- Resistance Band Work: Use resistance bands to perform lateral arm raises, which build strength in the supraspinatus and surrounding muscles.
For additional support with these techniques, consider therapeutic massage or acupuncture, which can help alleviate muscle tension and improve blood flow to the area. Both of these services are available at Athlete’s Choice Massage for those in Sherwood Park and Downtown Edmonton.
4. Professional Physical Therapy
A trained physical therapist can create a personalized program to safely strengthen the shoulder, promote flexibility, and prevent future injuries. Deep tissue massage can also help relieve muscle tension and enhance recovery.
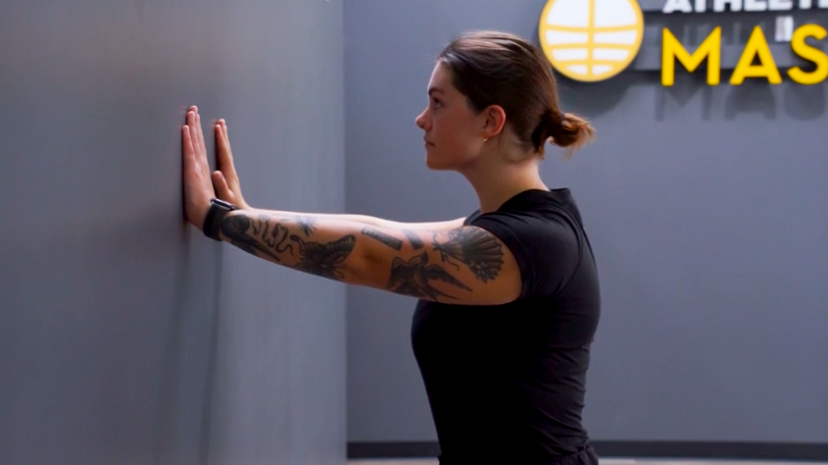

Preventing Future Supraspinatus Muscle Pain
Consistent maintenance of shoulder health is essential for active individuals. Incorporate the following preventive measures into your routine:
- Proper Warm-Up: Engage in a full warm-up before intense physical activities.
- Posture Correction: Maintain shoulder posture, especially during lifting, to avoid unnecessary strain.
- Regular Massage Therapy: Massage can reduce muscle tension, increase circulation, and support recovery—try a therapeutic massage session for targeted shoulder relief.
For active individuals based in Edmonton or Sherwood Park, Athlete’s Choice Massage offers a range of therapies designed to promote recovery and relieve pain. Proper management of supraspinatus muscle issues is key to sustaining an active lifestyle.
Final Thoughts on Managing Supraspinatus Muscle Pain
Addressing supraspinatus pain proactively allows active individuals in Edmonton and Sherwood Park to maintain their performance and reduce the risk of further injury. By incorporating a combination of stretching, strengthening, and professional therapies, you can support the long-term health and resilience of your shoulder.
For more information on therapies to alleviate supraspinatus muscle pain, visit Athlete’s Choice Massage locations in Downtown Edmonton or Sherwood Park.